+7 (929) 727 53 60 Traumatology / Orthopedics / Neurosurgery
Instructions: Preservation of the hole after tooth extraction. Additional manipulation
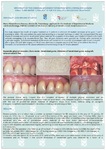
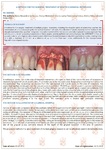
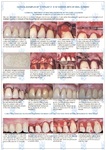
When a tooth is removed after revision of the hole, additional surgical manipulation is performed. Reticulofibrous cells located near the tooth holes are bone cells that are not fully mature and can manifest their potential in various ways. They are located just 5 places in the body: the seams of the skull, the bones of the skull are mobile throughout life; the corners of the mandible, which is associated with the location of the next temporomandibular joint; labyrinth of the inner ear, the place of attachment of tendons and ligaments, tooth holes. Also, this tissue is formed during an oncological process and during distant fusion of bone fragments that do not have tight contact. Therefore, we should take into account the following nuances: when a tooth is removed, it makes sense to release these reticulofibrous cells, respectively, in the area of the operation to trigger their activity and potential. We use a small-diameter drill bit from 0.8 to 1.2 mm, optimally 1 mm. The angle of entry of the drill is 30-45 degrees, as far as the bone edge of the tooth hole allows. The goal is to make pinholes inside the tooth, retreating 1 / 2-1 / 3 from the edge of the hole. The hole of the tooth should also always be stitched to form a volume of soft tissue in this area for the subsequent installation of implants.
-
Instructions: Interval of delayed implantation after sinus lift
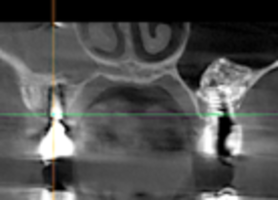 The waiting time depends on the baseline, volume and quality of the patient's bone in the sinuses, the condition of the soft tissues, the age of the patient, associated diseases and other factors.
Read more
The waiting time depends on the baseline, volume and quality of the patient's bone in the sinuses, the condition of the soft tissues, the age of the patient, associated diseases and other factors.
Read more
-
Instructions: Preparing the receiving bed when / before the complex DTR
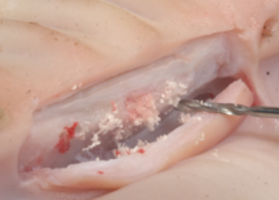 The purpose of manipulation: thinning of the cortical plate, access to osteogenic cells of spongiosa, alteration of deep cells of compact bone, launch of regenerative potentials
Read more
The purpose of manipulation: thinning of the cortical plate, access to osteogenic cells of spongiosa, alteration of deep cells of compact bone, launch of regenerative potentials
Read more
-
Instructions: The need to close lateral access during sinus lift
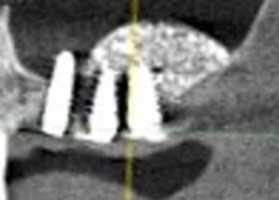 The risk of migration / loss of the bone bioimplant from the sinus and the contact of the split flap with the bone bioimplant require that the sinus window be closed with a membrane or bone plate.
Read more
The risk of migration / loss of the bone bioimplant from the sinus and the contact of the split flap with the bone bioimplant require that the sinus window be closed with a membrane or bone plate.
Read more
-
Instructions: Increase the volume of the attached gingiva with a Collagen membrane (dura mater)
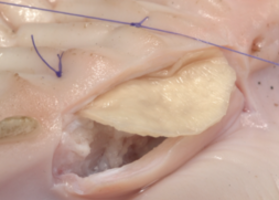 The purpose of the operation: the creation of the volume and thickness of the attached gingiva in the area of future bone grafting, an increase in the vestibule of the oral cavity, the launch of the patient's own regenerative potentials.
Read more
The purpose of the operation: the creation of the volume and thickness of the attached gingiva in the area of future bone grafting, an increase in the vestibule of the oral cavity, the launch of the patient's own regenerative potentials.
Read more